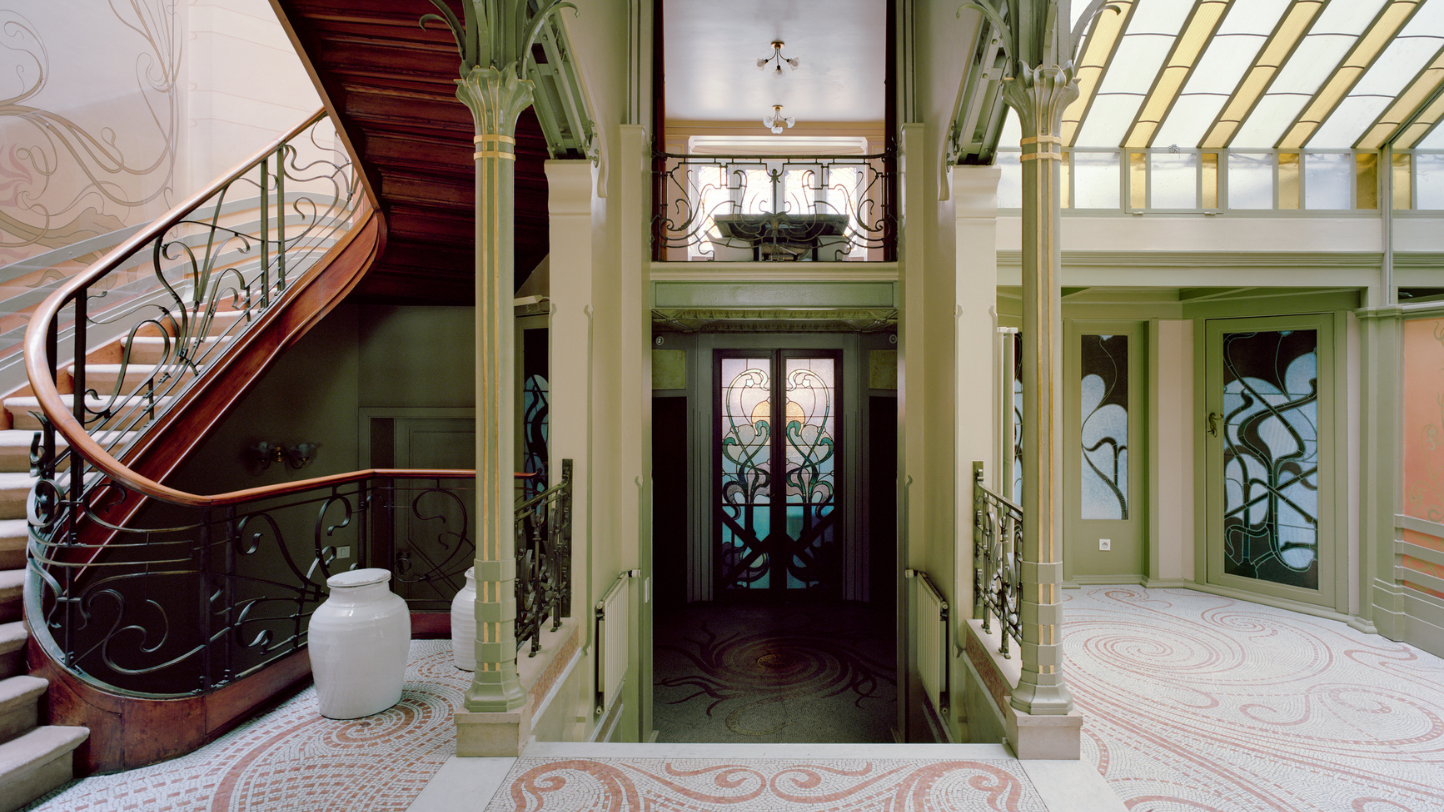
The history of the Art Nouveau movement
The Art Nouveau movement, also known as Art Nouveau, was an artistic and architectural style that emerged at the end of the 19th century and beginning of the 20th century. Originating in Europe, the movement spread to different countries and influenced various forms of artistic expression, including architecture, interior design, graphic design, decorative arts, fashion and visual arts.
The term "Art Nouveau" is of French origin and means "new art". The movement was characterized by the search for a new aesthetic language, moving away from predominant historical styles, such as neoclassicism and eclecticism. The artists and designers of the movement sought to create art that was innovative, modern, and inspired by nature.
New art was marked by organic and sinuous forms, curved lines, floral motifs, arabesques and stylized patterns. The influences of nature were often represented in the works, with elements such as flowers, plants, animals and fluid forms. Furthermore, symmetry was often avoided in favor of asymmetrical and asymmetrical compositions.
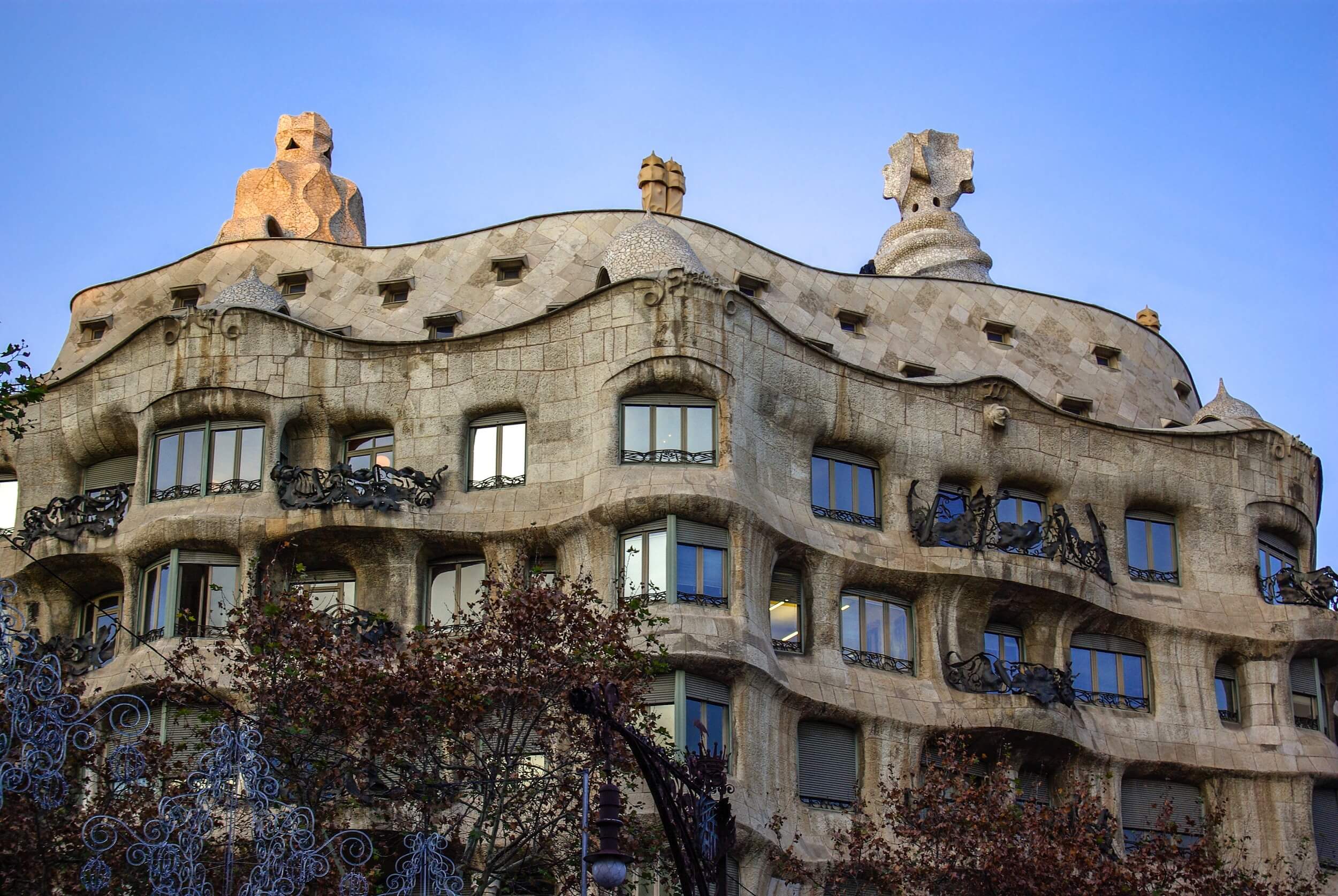
In architecture, the Art Nouveau style produced buildings characterized by ornate facades, extensive use of wrought iron and colored glass, large windows, extravagant decorative details, and a harmonious integration between the building's structure and decoration. Some famous examples of Art Nouveau architecture include the Casa Batlló and Casa Milà in Barcelona, designed by Antoni Gaudí, and the Paris Opera House, designed by Charles Garnier.
Although the movement was popular for a relatively short period, its influence was significant and helped pave the way for modernism in arts and design. Art Nouveau was an important movement in the transition between 19th century historicism and 20th century avant-gardes, leaving a lasting legacy in the history of art.

What are the characteristics of the works of the Art Nouveau movement?
Curved and sinuous lines: Art Nouveau valued organic, fluid and curved lines, in contrast to the straight and rigid lines of previous styles. These sinuous lines were inspired by nature and evoked a sense of movement and harmony.
Floral and natural motifs: Nature was a primary source of inspiration for Art Nouveau artists. The works featured a profusion of floral motifs, such as lilies, roses, leaves, as well as natural elements such as insects, birds and other stylized animals.
Detailed ornamentation: The movement was noted for its rich ornamentation and minute detailing. Art Nouveau artists applied elaborate decorative patterns, with intertwining and stylized shapes that covered the entire surface of works, including walls, furniture, objects and even jewelry.
Use of modern materials: Although Art Nouveau valued ornamentation and decoration, it also embraced the use of modern materials such as wrought iron, colored glass, ceramics, metal, and reinforced concrete. These materials were often incorporated into works in innovative and expressive ways.
Vibrant and contrasting colors: Colors played an important role in Art Nouveau works. Vibrant and contrasting tones were used to create visual impact and highlight the ornamental details. The use of bold, rich color palettes gave the works an exuberant appearance.
Integration between art and crafts: The Art Nouveau movement sought integration between art and crafts. Artists valued the idea that all forms of artistic creation, from architecture to jewelry, were equally important and deserved careful attention to detail and aesthetics.

Who were your most famous artists?
Alphonse Mucha (1860-1939): The Czech artist Alphonse Mucha is considered one of the main exponents of the Art Nouveau style. He became known for his decorative posters featuring graceful women surrounded by floral ornaments and curved waves.
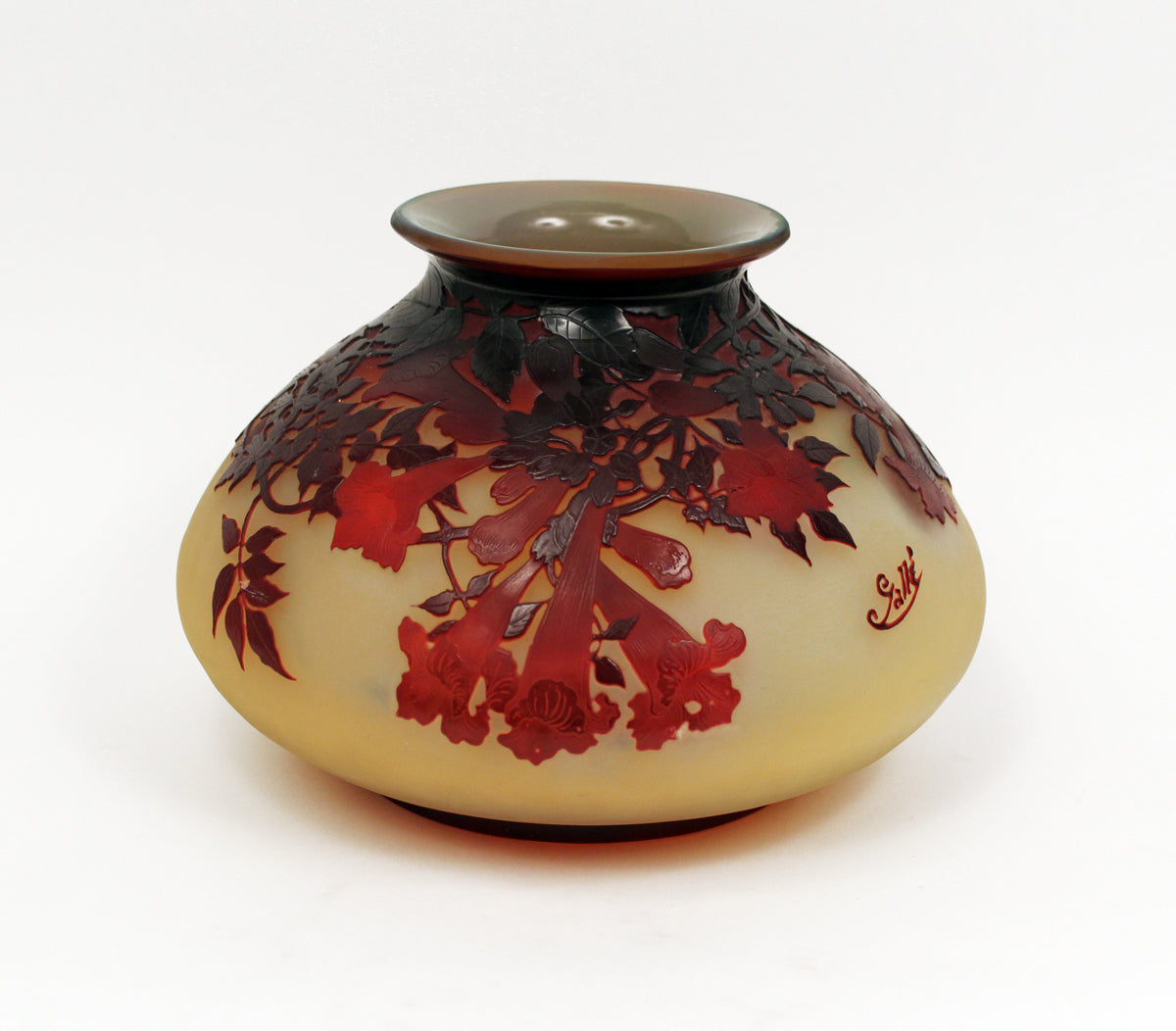
Émile Gallé (1846-1904): Émile Gallé was a French glass designer and manufacturer, known for his art glass pieces in the Art Nouveau style. He used innovative blown and engraved glass techniques, often incorporating natural elements, such as flowers and insects, into his creations.
Hector Guimard (1867-1942): Hector Guimard was a French architect and designer who stood out for his architectural creations and furniture in the Art Nouveau style. He became known for designing the iconic Paris metro entrances.
Antoni Gaudí (1852-1926): Although often associated with Catalan modernism, Antoni Gaudí was also influential in the Art Nouveau movement. The Spanish architect is famous for designing extraordinary buildings in Barcelona, such as Casa Batlló and Casa Milà, which feature organic shapes and decorative details characteristic of the Art Nouveau style.
Gustav Klimt (1862-1918): Although he worked mainly in Austria, Klimt was also influential in the Art Nouveau movement. His works were known for their stylized female figures, ornamental details and the use of gold leaf. His most famous painting, "The Kiss", is an iconic example of the Art Nouveau style.
René Lalique (1860-1945): René Lalique was a French jeweler and glass designer whose glass and jewelry creations are highly valued to this day. His pieces were known for their delicacy, detailed style and incorporation of natural motifs, such as flowers and dragonflies.

What are the most famous architectural works?
Casa Batlló and Casa Milà (La Pedrera) - Barcelona, Spain: Both designed by renowned architect Antoni Gaudí, these homes are stunning examples of Art Nouveau architecture. Casa Batlló features an undulating facade with colorful ceramic and wrought iron details, while Casa Milà has a sculptural facade and undulating roofs.
Buildings designed by Latvian architect Mikhail Eisenstein are most famous examples of Art Nouveau in Riga. It became known for its facade decorated with floral motifs, female figures and intricate details.
Majolikahaus - Vienna, Austria: Designed by architect Otto Wagner, the Majolikahaus is a residential building that displays characteristic elements of the Art Nouveau style, such as floral ornamentation, colorful tiles and curvilinear details.
Hotel Tassel - Brussels, Belgium: Designed by Victor Horta, Hotel Tassel is often considered one of the earliest examples of Art Nouveau architecture. It features an elegant facade with curved lines, colorful stained glass, wrought iron and a harmonious integration between the building structure and decoration.
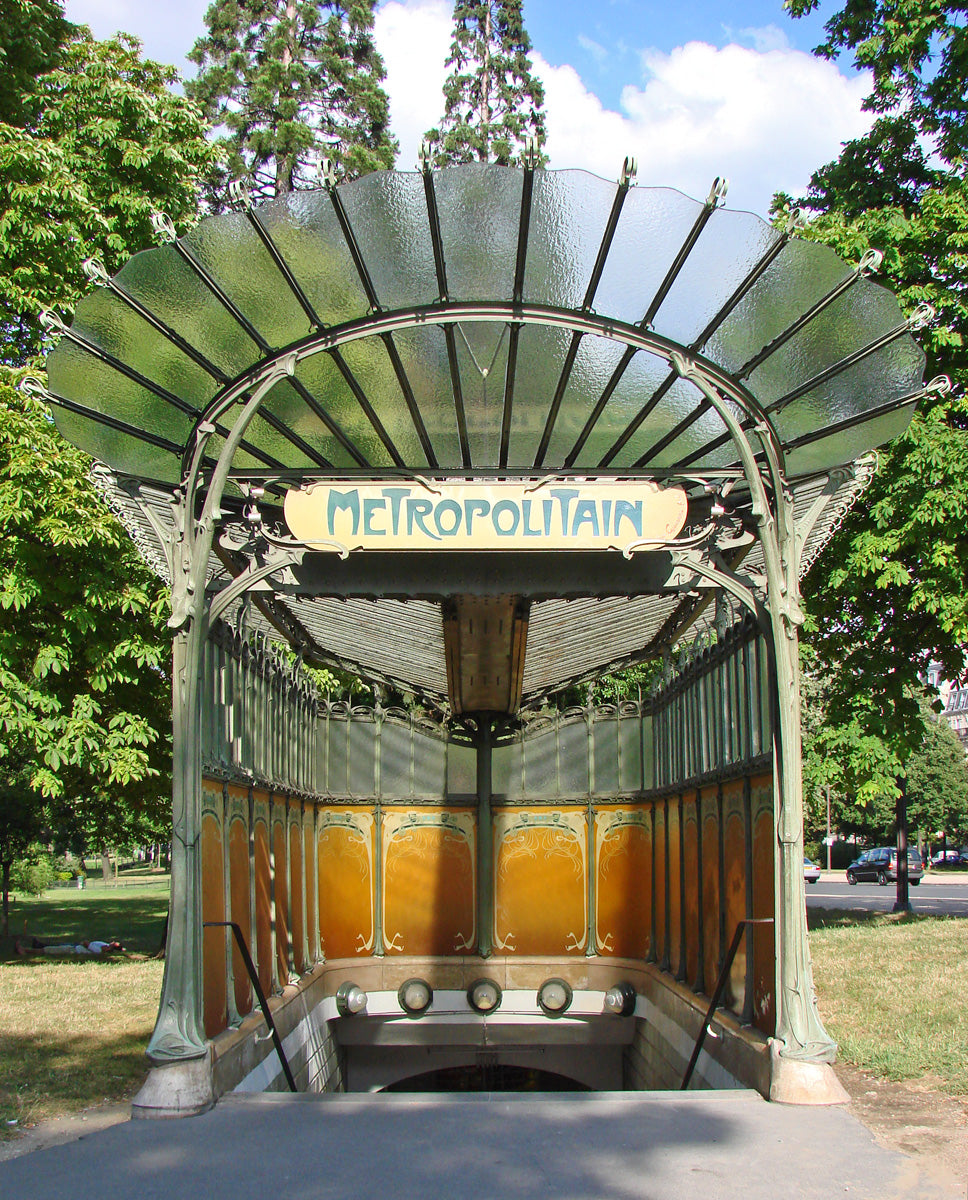

What is the legacy of Art Nouveau?
Art Nouveau, also known as Art Nouveau, left a significant legacy in the areas of art, architecture, design and aesthetics. Here are some of the lasting contributions and influences left by the movement:
Aesthetic innovation: Art Nouveau brought a new visual and aesthetic language to the world of art and design. Breaking away from traditional 19th-century styles such as neoclassicism and eclecticism, the movement introduced organic shapes, curved lines, detailed ornaments, and an emphasis on nature. This innovative approach influenced later movements such as Art Deco and modernism.
Integration between art and crafts: Arte Nova valued the fusion between art and craftsmanship, seeking to elevate the importance of design and everyday objects. Artists and designers in the movement worked across disciplines, including architecture, furniture, jewelry, glass, ceramics, and textiles, promoting the idea that all forms of artistic creation deserve careful attention to detail and aesthetics.
Use of modern materials and innovative techniques: Art Nouveau embraced the use of modern materials such as wrought iron, colored glass, ceramics and reinforced concrete. Artists and architects experimented with new techniques for producing and applying these materials, resulting in bold and expressive creations.
Nature involvement: Nature played a central role in the aesthetics of Art Nouveau. Floral motifs, organic shapes and the stylized representation of flora and fauna were distinctive elements of the movement. This appreciation of nature as a source of aesthetic inspiration influenced various forms of artistic expression and design throughout the 20th century.
Architecture Expansion: Art Nouveau brought an innovative approach to architecture, rejecting the rigidity of traditional forms. The movement's architects explored the harmonious integration between the building's structure and decoration, creating ornate facades, curvilinear details and new spatial solutions. The Art Nouveau architectural style influenced future movements, such as modernism, and left a mark on the urban landscapes of many cities.
Valuing accessible design: Art Nouveau sought to make design accessible to a wider public, leaving the exclusive sphere of the elite. This resulted in the production of decorative objects, furniture and clothing items that combined aesthetics and functionality, while being produced on a large scale. This democratic approach to design influenced the Arts and Crafts movement and had a lasting impact on industrialized production in the 20th century.
The legacy of Art Nouveau can be seen in many aspects of contemporary culture. His distinctive style and search for an innovative visual language continue to inspire artists, designers and architects around the world, keeping the influence of this revolutionary movement alive.