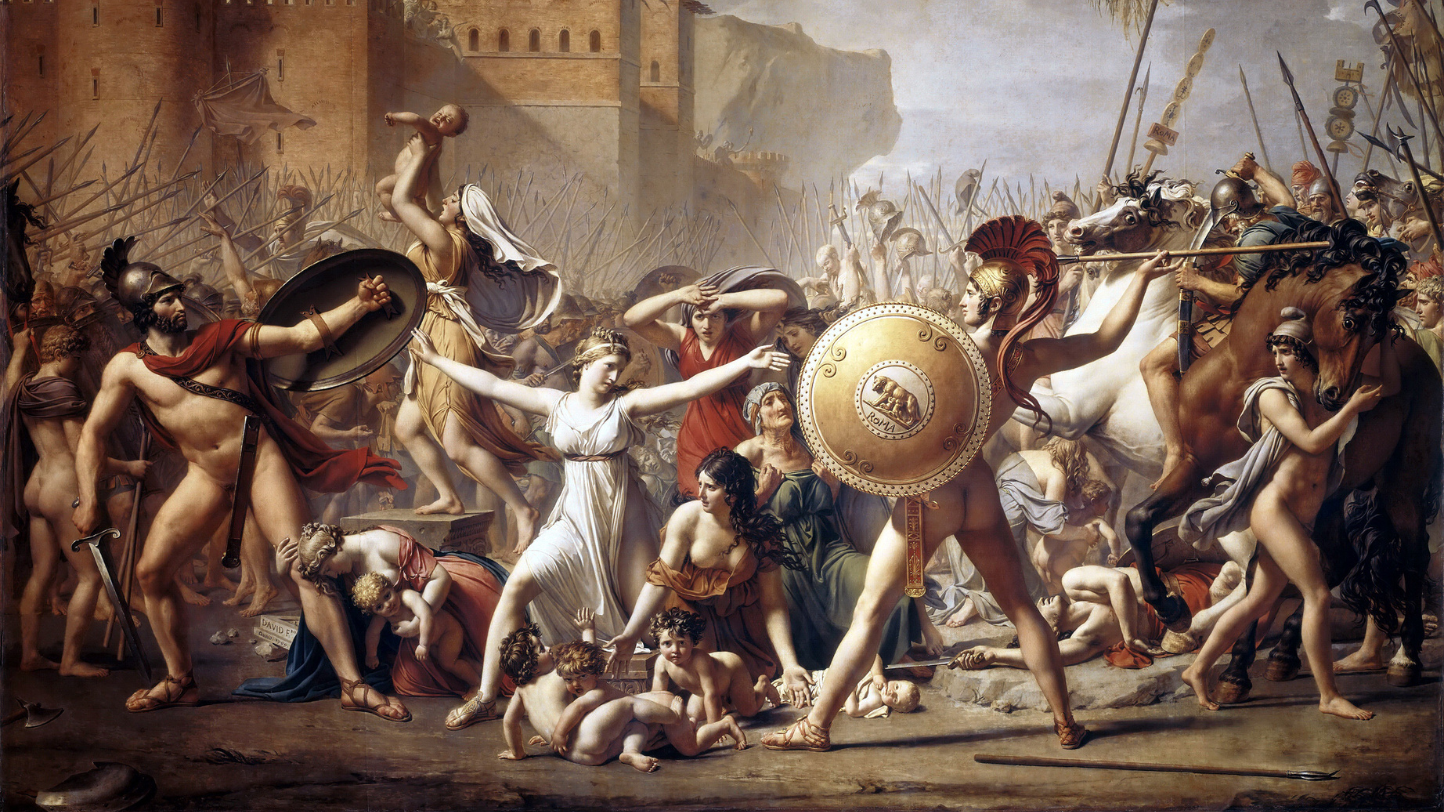
What was Neoclassicism?
Neoclassicism was an artistic and cultural movement that emerged in the 18th century as a reaction to the baroque and rococo styles prevalent at the time. It was inspired by the ideals of Greco-Roman classical antiquity and sought a return to the forms and aesthetic principles of that period.
The neoclassical movement spanned many areas, including literature, architecture, sculpture, painting, music, and design. Neoclassical artists sought a more rational, balanced and symmetrical aesthetic, in contrast to the ornamental and extravagant style of the Rococo. They were inspired by the works of the great artists of antiquity, such as the Greek sculptors Phidias and Praxiteles and the Roman painters Raphael and Poussin.
In the field of architecture, Neoclassicism sought to revive the forms and proportions of Greek and Roman architecture, with an emphasis on simplicity, harmony and order. Neoclassical buildings feature columns, gables, symmetry, and mathematically precise proportions.
In painting, neoclassical artists sought to represent historical, mythological and religious themes with clarity and serenity. They valued precision in detail, the use of light and shadow, and balanced composition. Great neoclassical painters include Jacques-Louis David, Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres and Antonio Canova in sculpture.
In literature, Neoclassicism sought to rescue the simplicity and clarity of ancient poetry and prose. Neoclassical writers valued logic, reason and morality in their works, often imitating models from classical antiquity.
Neoclassicism exerted a significant influence on European art and culture in the 18th and early 19th centuries, reflecting the ideals of the time, which were marked by the search for order, reason and stability after the excesses and exuberance of the Baroque period. However, the movement was also criticized for its rigidity and lack of originality, eventually being replaced by other artistic currents, such as Romanticism.
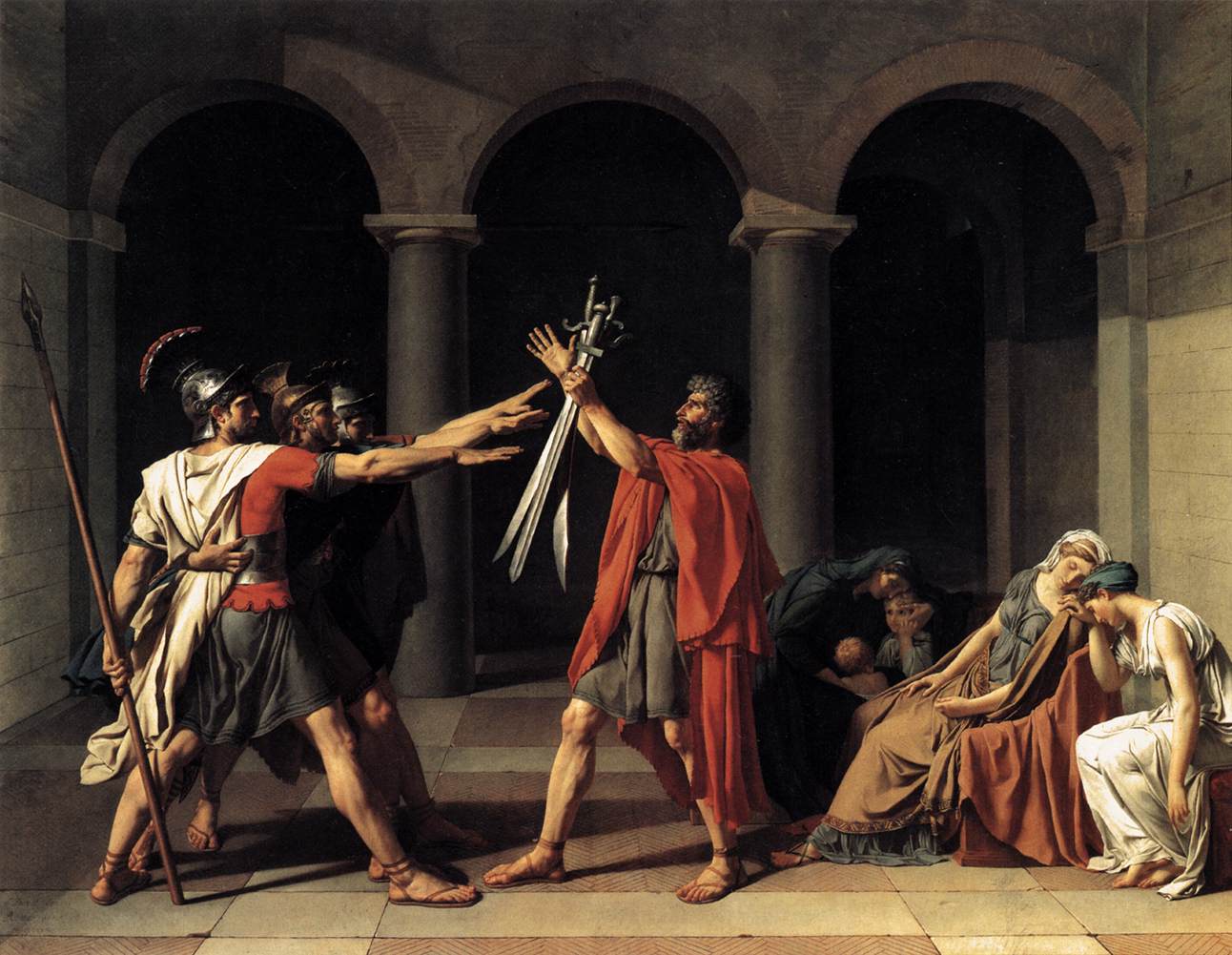

What are the characteristics of Neoclassicism?
Characteristics of Neoclassicism include:- Influence of classical antiquity: Neoclassicism was heavily influenced by the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome. Artists sought to revive the forms, themes and aesthetic ideals of these civilizations.
- Balance and harmony: Neoclassicism valued order, clarity and symmetry. The works were carefully planned and balanced, following mathematically precise proportions.
- Simplification and rationality: In contrast to the ornamental and extravagant style of the Rococo, Neoclassicism sought simplicity and rationality. The forms were simplified and stripped of decorative excesses.
- Historical and mythological themes: Neoclassical artists often chose themes from Greek and Roman mythology, as well as important historical events, for their works. They were inspired by the stories and figures of classical antiquity, to transmit moral and heroic values.
- Accuracy and detail: Neoclassical artists valued precision in detail and the careful depiction of anatomy and proportion. They sought to achieve a realistic but idealized representation of the subjects they portrayed.
- Use of light and shadow: Neoclassicism also employed light and shadow techniques to create three-dimensional effects and highlight the objects represented. This contributed to the sense of depth and realism in the works.
- Emphasis on morality and virtue: Neoclassical artists often sought to convey moral messages and exemplify virtues in their works. They portrayed heroic figures, saints, gods and historical scenes as examples of virtuous conduct. These characteristics helped to define the Neoclassicist style and to distinguish it from earlier and later artistic styles, reflecting the quest for order, reason and balance in 18th-century Europe.
Who were the main artists?
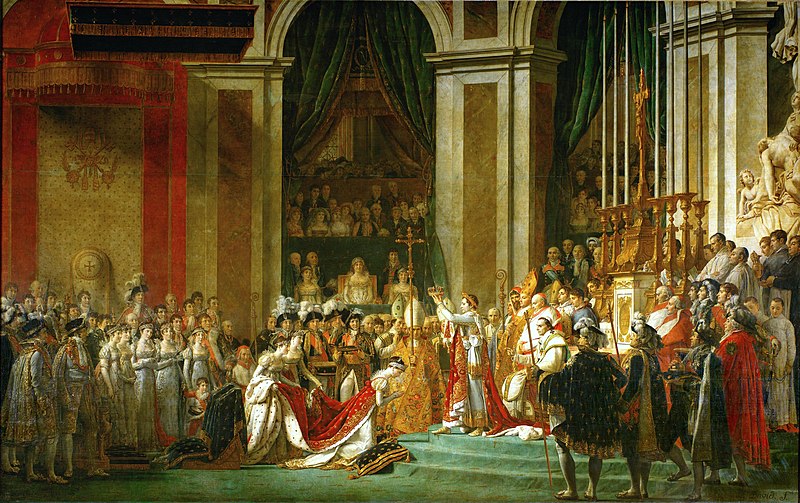
Some of the main neoclassical artists are:- Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825): Considered the leading neoclassical painter, David produced iconic works such as "The Death of Marat" and "The Coronation of Napoleon". He was known for his technical precision, clear composition, and idealized portraits.
- Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres (1780-1867): Ingres was a French painter known for his classical figures and detailed portraits. His works, such as "The Great Odalisque" and "The Turkish Bath", stood out for their precision and elegance.
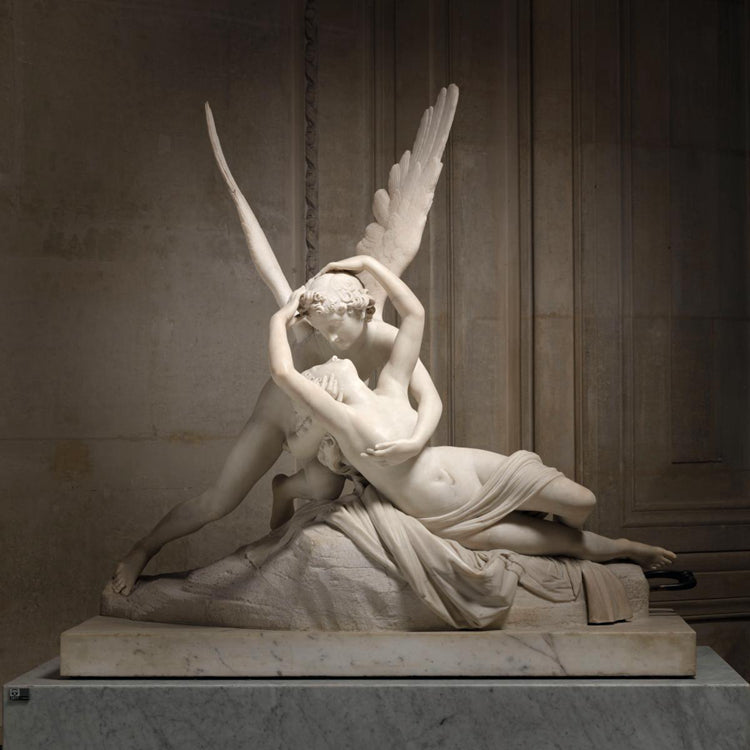
- Antonio Canova (1757-1822): He was an Italian sculptor renowned for his neoclassical work. His sculptures, such as "Psyche Revived by the Kiss of Love" and "Cupid and Psyche", displayed a combination of technical skill and restrained emotion.
- Angelica Kauffman (1741-1807): She was a Swiss painter who stood out for her portraits and neoclassical historical scenes. She was known for her ability to represent female figures, in addition to being one of the few recognized female artists during the period.
- Thomas Jefferson (1743-1826): Though best known as the third president of the United States, Thomas Jefferson was also an influential architect and proponent of Neoclassicism. He designed the University of Virginia, inspired by classical Roman architecture. These are just a few examples of leading neoclassical artists. The movement had influence across Europe and beyond, with artists from different countries contributing to the development and spread of the neoclassical style.
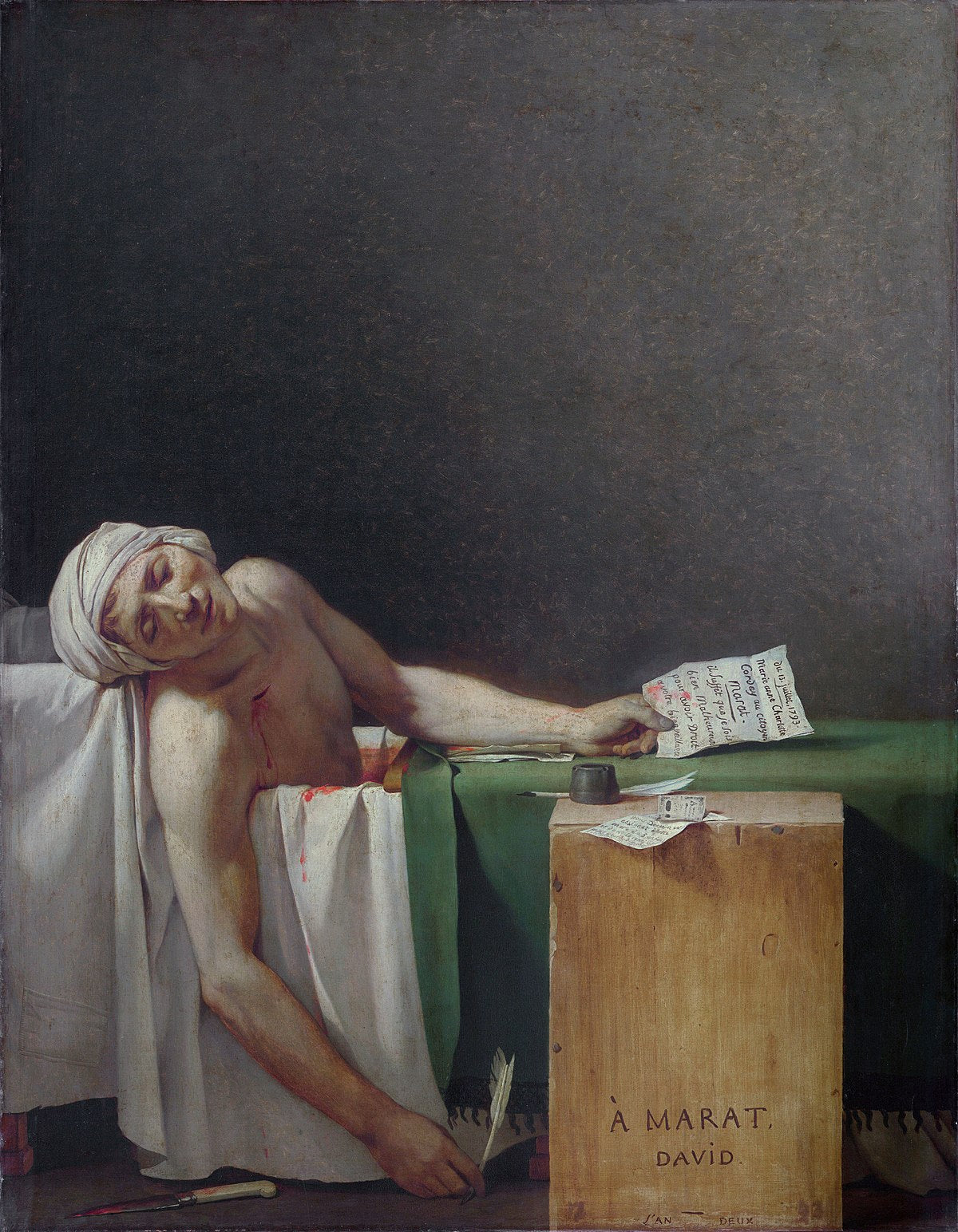

What aspect of Greek culture is reflected in the neoclassical architecture still in use today?
A fundamental aspect of Greek culture that is reflected in neoclassical architecture to this day is the use of classical architectural elements such as columns, pediments, mathematical proportions and symmetry.
Greek columns, in particular, play a prominent role in neoclassical architecture. There are three main styles of Greek columns: Doric, Ionic and Corinthian. Each style has distinct characteristics, such as the shape and ornamentation of the columns. These styles were adopted by neoclassical architects and continue to be used in architecture today, both in public and residential buildings.
In addition to columns, triangular pediments are another characteristic element of Greek architecture that remains present in neoclassical architecture. Gables are triangular structures located at the top of building facades, usually adorned with sculptures or reliefs.
Mathematical proportions and symmetry are principles that also continue to be applied in contemporary neoclassical architecture. The architects seek to create visual harmony and balance through the use of precise and symmetrical proportions, following the guidelines established by the ancient Greeks.
These elements of neoclassical architecture, inspired by Greek culture, are appreciated for their classic and timeless aesthetic, as they impart a sense of solidity, order and elegance to buildings, making them an integral part of the architectural style to this day.

What are the most famous works of the neoclassical movement?
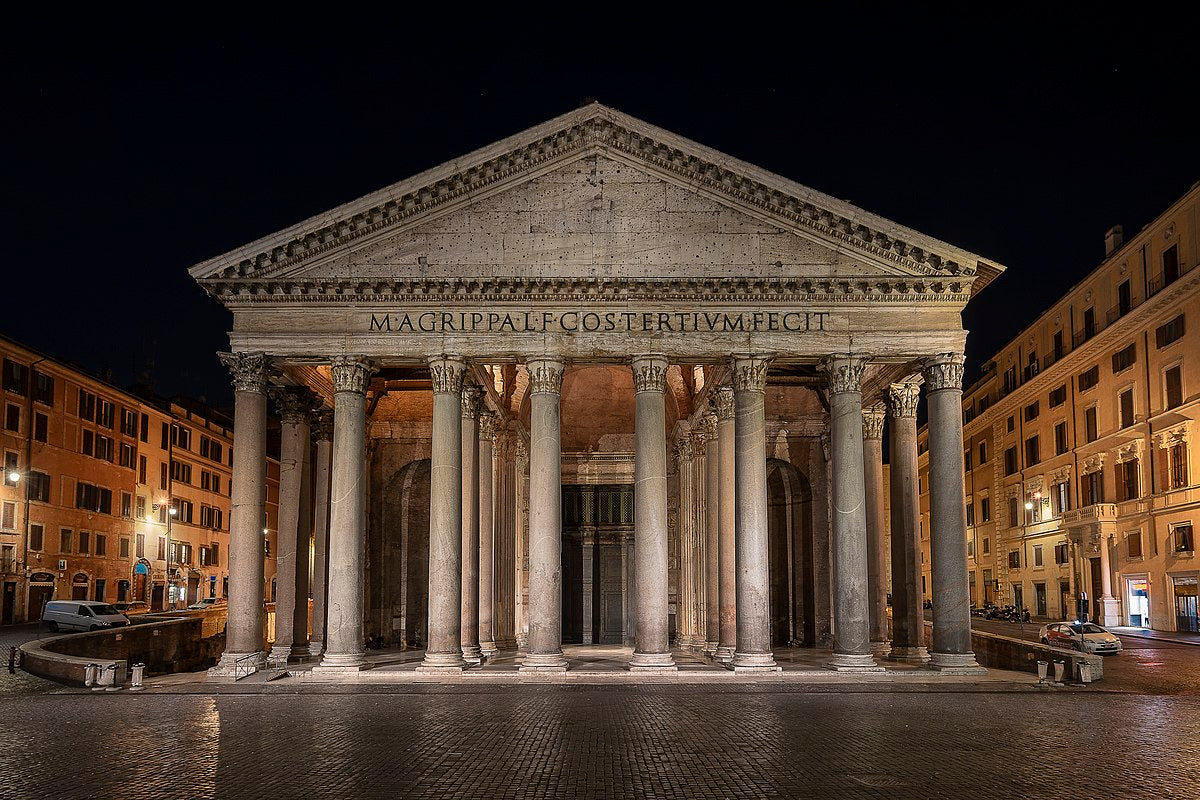
The neoclassical movement produced several famous works in different art forms. Here are some of the most well-known works of the neoclassical movement:- The Pantheon (Rome, Italy): One of the most famous examples of neoclassical architecture, although an ancient Roman structure, it influenced many subsequent neoclassical buildings.
- The Capitol (Washington, DC, USA): Designed by William Thornton and Charles Bulfinch, it is an iconic government building in the United States, inspired by classical Greek and Roman architecture.
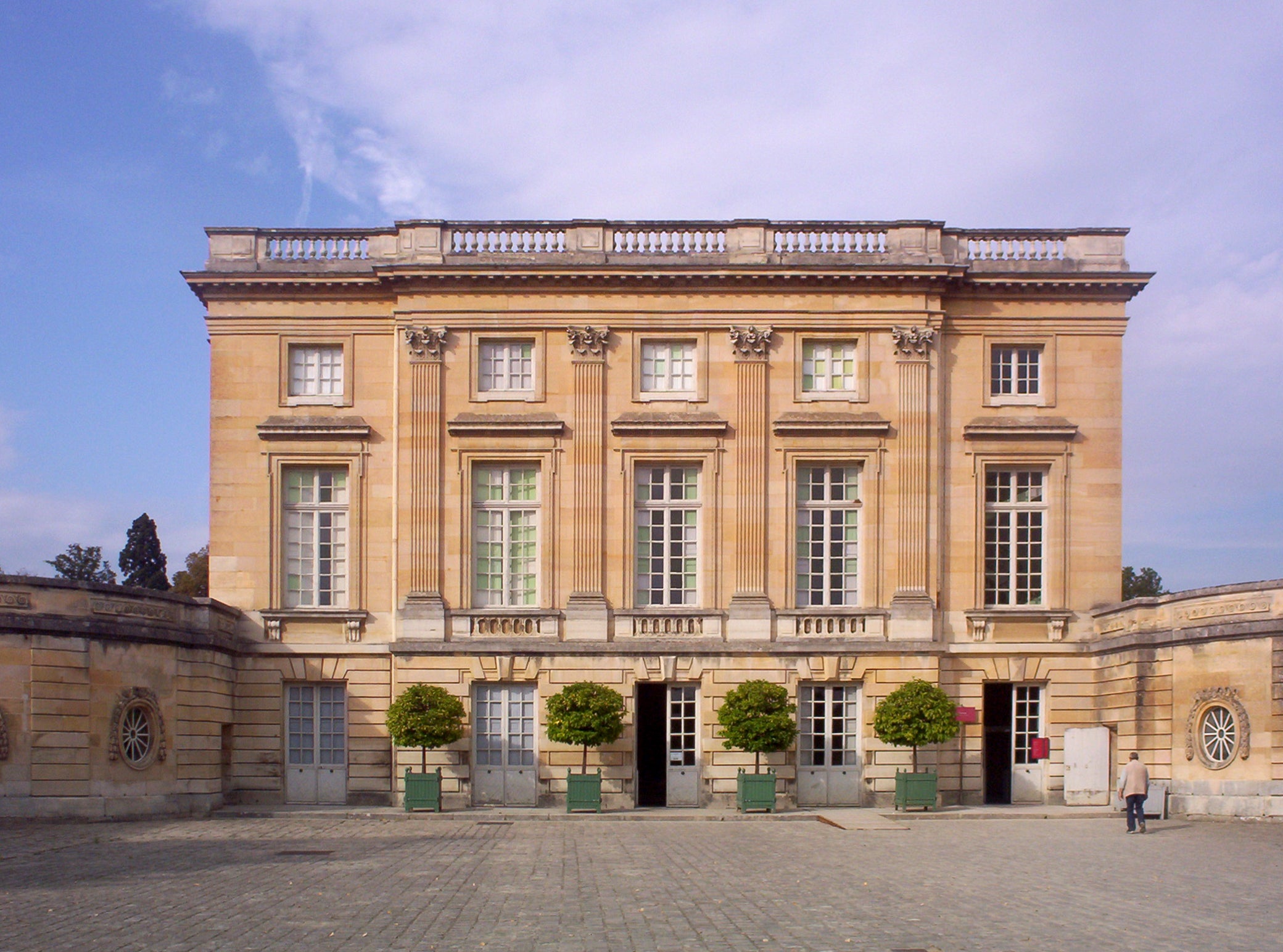
- The Petit Trianon (Versailles, France): A small neoclassical palace in the complex of Versailles, designed by Ange-Jacques Gabriel, which served as a refuge for Queen Marie Antoinette.
- "Venus de Milo": A marble sculpture depicting the goddess Venus, dating from the 2nd century BC, which was rediscovered during the neoclassical movement and became one of the icons of the time.
- "Psyche and Cupid" (Antonio Canova): A marble sculpture depicting the moment when Cupid kisses Psyche, creating a work of great beauty and expression.
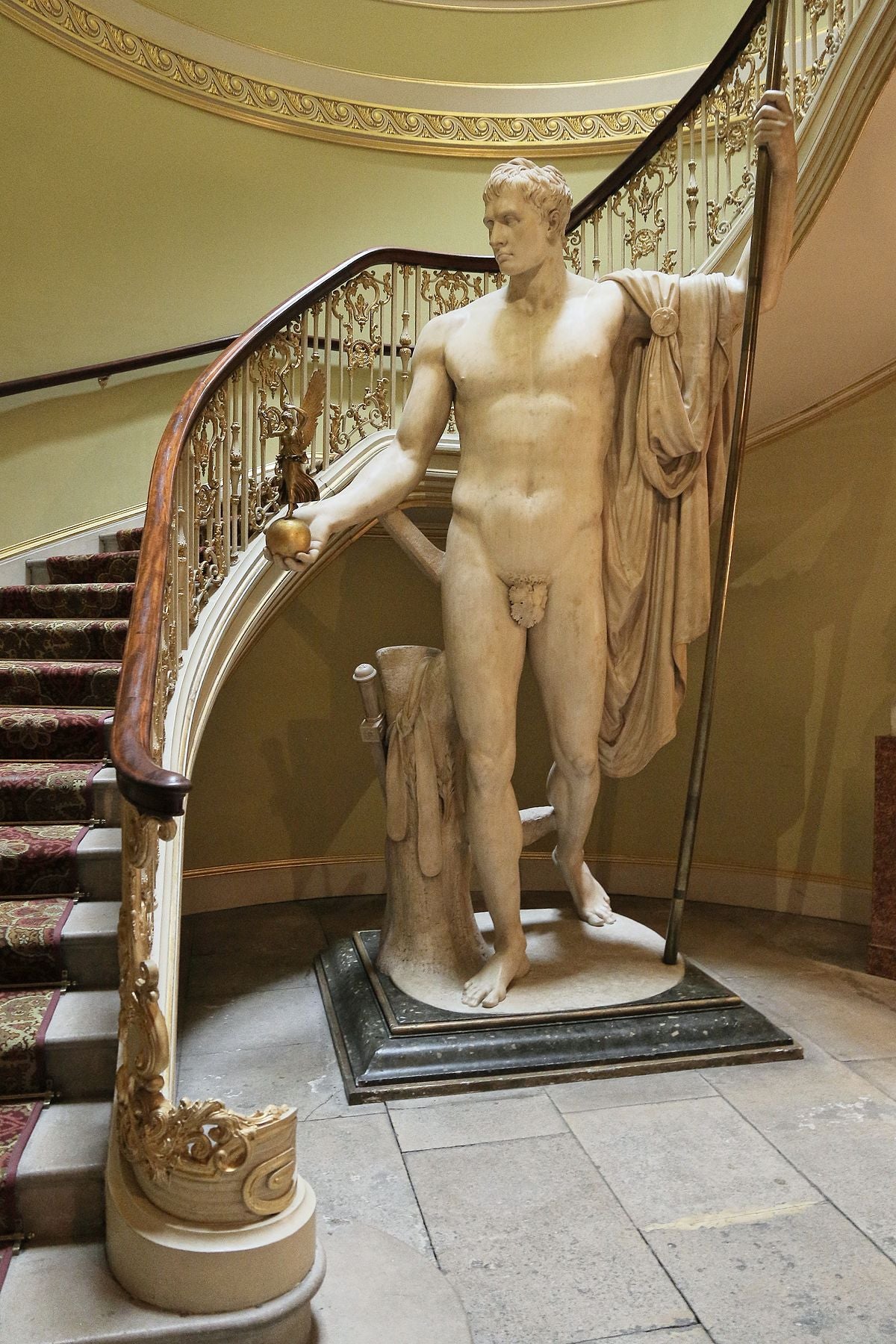
- "Napoleon as Mars the Peacemaker" (Antonio Canova): A sculpture of Napoleon Bonaparte as the god of war, depicting him as a military leader and peacemaker.
- "The Death of Marat" (Jacques-Louis David): A painting depicting the tragic death of Jean-Paul Marat, French revolutionary leader, with a dramatic and heroic depiction.
- "The Oath of the Horatii" (Jacques-Louis David): A work that represents the story of the Horatii, three Roman brothers who swore to defend Rome to the death, symbolizing duty and sacrifice for their homeland.
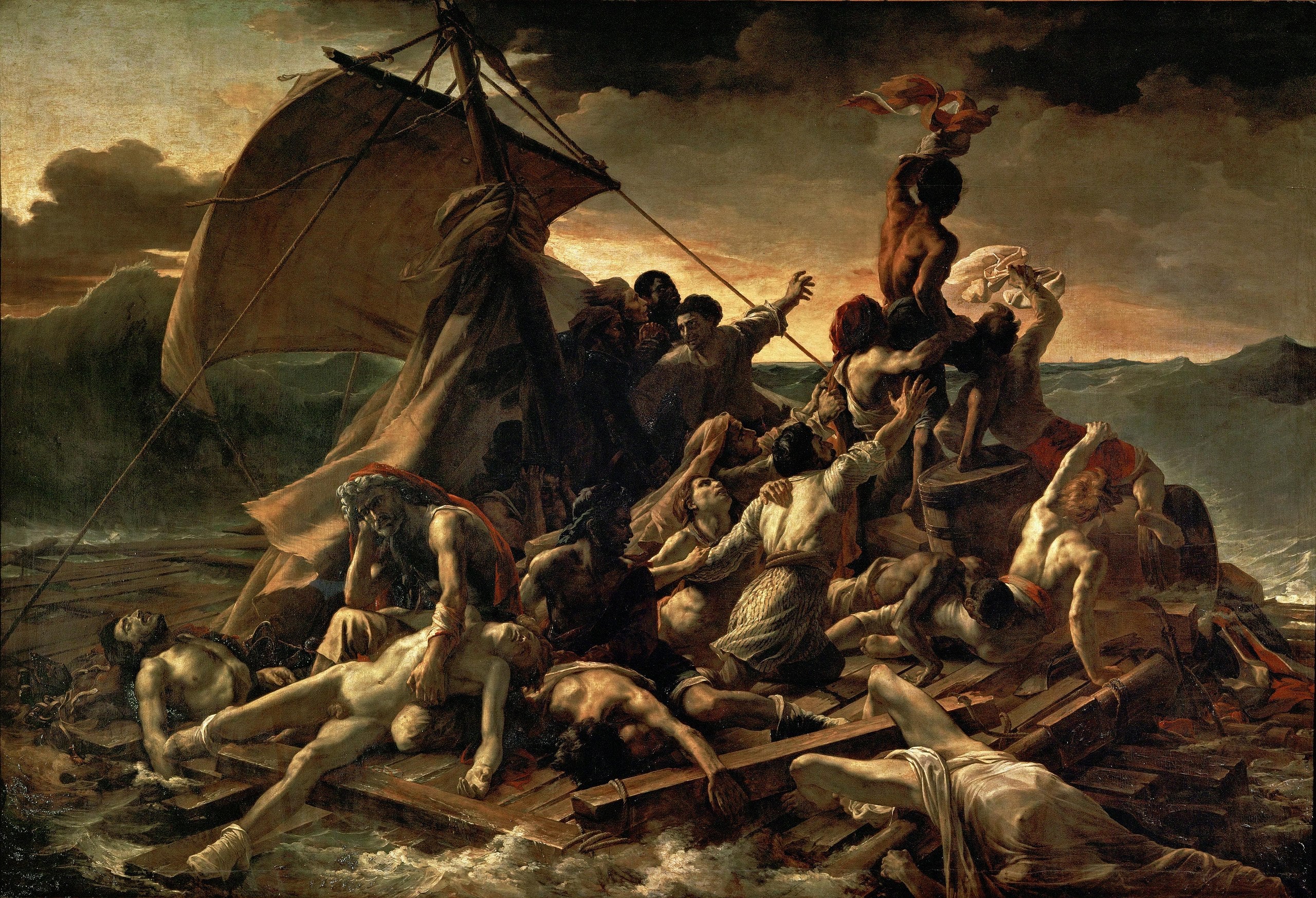
- "The Raft of the Medusa" (Théodore Géricault): A painting depicting the sinking of the French frigate Medusa, where the survivors struggle for survival in a tragic situation. These are just some of the most famous works of the neoclassical movement, which encompassed many art forms. Each work reflects the aesthetic, thematic and historical ideals of the Neoclassical period.
Architecture:

Sculpture:

Painting:

How did Neoclassicism appear in Portugal?
Neoclassicism emerged in Portugal during the 18th century, influenced by artistic and cultural currents that occurred in Europe. In the Portuguese context, Neoclassicism was introduced mainly through contact with other European nations, such as France and Italy.
The arrival of Neoclassicism in Portugal is associated with the reign of King Dom José I (1750-1777) and, later, of his daughter, Dona Maria I (1777-1816). During this period, the Portuguese court established close ties with France, especially through the marriage of Dona Maria I to Prince D. Pedro de Bragança, future King Dom Pedro III.
This connection with France allowed the importation of neoclassical ideas and contact with French artists and intellectuals, who exerted great influence in the dissemination of the movement in Portugal. Portuguese artists traveled to Paris to study and absorb the neoclassical trends of the time, returning to the country to spread the style.
Portuguese Neoclassicism was also influenced by the rediscovery and revaluation of classical antiquities in Pompeii and Herculaneum, Italy, during the 18th century. Archaeological excavations of these Roman cities buried by the Vesuvius volcano have revealed a wealth of classical art and architecture, serving as a source of inspiration for Portuguese neoclassical artists.
One of the main names of Neoclassicism in Portugal was the architect and sculptor Joaquim Machado de Castro (1731-1822). He was responsible for important neoclassical projects in Portugal, including the reconstruction of Praça do Comércio in Lisbon, which became a landmark example of neoclassical architecture in the country.
Other Portuguese artists and architects, such as Carlos Mardel and Vicente Nunes, also embraced Neoclassicism and left their mark on the development of this style in Portugal.
Neoclassicism in Portugal had a significant presence in the field of architecture, sculpture and painting, with the construction of public buildings, monuments and works of art that followed neoclassical aesthetic principles. However, it is important to note that the neoclassical movement in Portugal was influenced by the cultural and historical characteristics of the country, incorporating local elements in its artistic expression.